
Declination measures how far overhead an object will rise in the sky, and is measured as 0° at the equator, +90° at the North Pole and -90° at the South Pole. There are 60 arc-minutes in a degree and 60 arc-seconds in an arc-minute. 0 hours RA is by convention the right ascention of the Sun on March 21, the vernal equinox.ĭeclination is measured in degrees (°), arc-minutes (') and arc-seconds ("), and is similar to latitude on Earth. Astronomical phenomena help define our idea of time, and the measurement of time. If you wait 5 hours, Cancer will be directly overhead (9 hrs - 4 hrs). of Right Ascension are hours, minutes, and seconds, just like time. The constellation Cancer has a RA of 9h (9 hrs). For example, the constellation Orion has a Right Ascension (RA) of 4 hours, which is where the center of the constellation appears directly overhead. As the Earth rotates, stars appear to rise in the East and set in the West just like the Sun. Right Ascension is measured in hours (h), minutes (m) and seconds (s) and is similar to longitude on Earth. They are similar to the system of longitude and latitude used to locate places on Earth. Geological Survey for their help in answering this question.Right Ascension and Declination are a system of coordinates used in astronomy to determine the location of stars, planets and other objects in the night sky. Naval Observatory and Brent Archinal of the U.S. Astronomers measure right ascension eastward along the celestial equator, starting from the Sun’s position at the spring equinox (also known as the first point in Aries). Today, only right ascension survives in astronomy, although the other terms find occasional use in astrology texts.
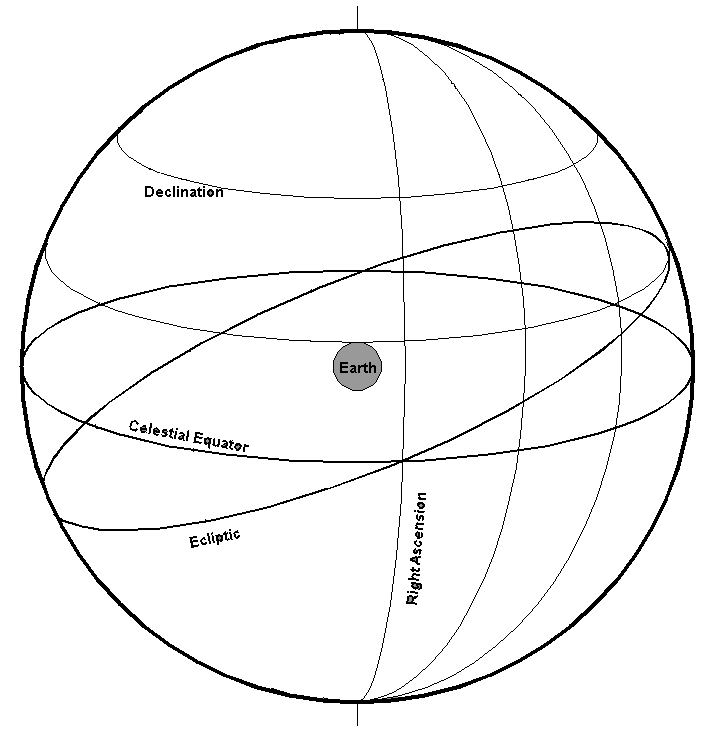
While “ascension” refers to rising stars, astronomers once also used right and oblique “descensions” based on setting stars. What does RA stand for RA stands for Right Ascension (astronomy) Suggest new definition This definition appears very frequently and is found in the following Acronym Finder categories: Science, medicine, engineering, etc. Oblique ascension refers positions to the horizon, so a given value applies only to observers at the same latitude, whereas right ascension describes sky positions for any observer on Earth.
Right ascension definition astronomy professional#
The term is now used so rarely that many professional astronomers have never heard of it. It is analogous to (but not the same as) longitude. Astronomers once referred to “oblique ascension,” an angle measured along the celestial equator from the spring equinox to where a point of interest meets the horizon. The second coordinate in the celestial equatorial system is right ascension. Now the celestial equator meets the horizon at an oblique angle, that is, one other than 90°. An objects right ascension is measured as an angle from the first point of. The stars now rise at a right angle to the horizon, and all objects on the same arc of right ascension rise together.īut suppose we move away from Earth’s equator. Compared to the definition for a solar day, a sidereal day is much easier to. This orientation makes the celestial sphere a “right sphere,” one in which the horizon meets the celestial equator at 90°. If we viewed the sky from Earth’s equator, the celestial poles would lie on the horizon and the celestial equator would arc directly overhead, passing through the zenith.


Astronomers measure right ascension eastward along the celestial equator, starting from the Sun’s position at the spring equinox (also known as the “first point in Aries”). A 15° span of the celestial equator equals the sky’s westward motion in one hour of time, and thus one hour of right ascension. Earth’s equator, projected onto the sphere, becomes the celestial equator lines of declination in the sky match up with parallels of earthly latitude. Earth floats in the center of this sphere so that its spin axis aligns with the North and South Celestial Poles. Imagine the sky as the inside surface of an enormous sphere. The observational difference between a star that displays proper motion only (left), and one that shows a parallax (right). Right ascension and declination together form the widely used equatorial coordinate system with which astronomers describe the positions of celestial objects. The concept dates at least from the time of Hipparchus (190-120 b.c.). Right ascension is based on the apparent rotation of the sky as Earth spins - 360° in 24 hours, or 15° per hour.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
